When to use pulsed TIG welding?
 Nov. 08, 2022
Nov. 08, 2022
Pulsed TIG Welding
Pulsed TIG welding is a special TIG welding technique in which the waveform of the welding current is intermittent and discontinuous, and the current size varies. This technique is mainly used to improve control of thin metal workpieces and prevent burn-through metal. The heat can be adjusted during the welding process by a foot pedal or by setting the pulse frequency to ensure that there is enough heat at the weld without adding too much filler metal or burning through the metal. Pulsed TIG welding is particularly suitable for situations where fine control of heat input is required, such as welding products such as FPC (flexible printed circuits), PCB (printed circuit boards), LED displays, circuit boards, and connectors.
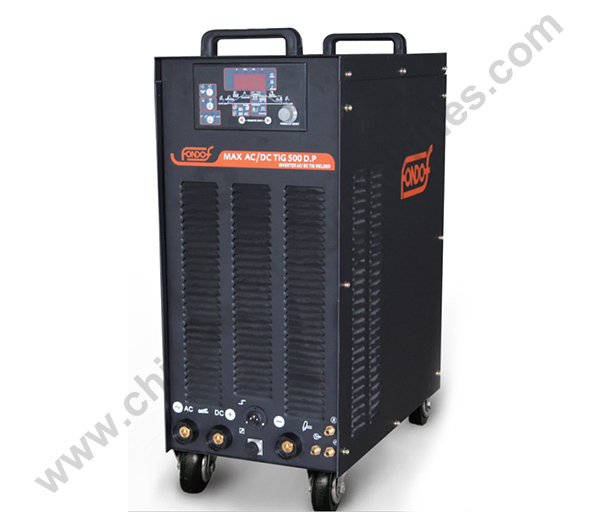
Pulse TIG Welders
Pulse TIG welders usually refer to devices that divide sinusoidal alternating current into several current segments through silicon-controlled rectifiers, also known as pulse welders. This type of welder can better control the heat during the welding process and avoid excessive filler metal entering the weld or burning through the metal. Pulsed TIG welders are widely used in situations where high-precision and beautiful welds are required, such as aerospace, automotive manufacturing, and precision instrument manufacturing. When using a pulse TIG welder, different welding effects can be achieved by setting different pulse frequencies, improving welding quality and production efficiency.
Double Pulse Welding
Double pulse welding is an advanced form of pulse TIG welding. By alternating two pulse currents of different frequencies during the welding process, the welding quality can be further improved. This method is particularly suitable for welding heat-sensitive materials such as aluminum alloys, because the heat distribution can be precisely controlled to reduce the heat-affected zone and avoid overheating and deformation of the material. Double pulse welding technology can also achieve a more uniform molten pool flow, making the weld smoother and more beautiful. In some specific application scenarios, such as welding thin-walled structures or parts with complex shapes, double pulse welding can provide better control and flexibility.
Pulsed means that the waveform of the welding current is intermittent and discontinuous, and the current size varies. Generally speaking, the commonly referred to Ac pulse TIG welder refers to the division of sinusoidal alternating current into several segments of current through silicon controlled, commonly known as pulse welder. Pulse welder is mainly used to weld FPC, PCB, LED display, lineup, terminals and other products. Pulse welding with TIG welder has some very special applications and sometimes it can come in handy to get the job done better. Here are some TIG welding applications with pulses.
Better Control of Heat
Pulsing for TIG is designed to improve your control when you don't want to burn through the metal workpiece. Using a pedal or setting the pulse will moderate the heat as you weld, ensuring that there is enough heat in the weld joint without putting a lot of filler metal into the joint or burning through the metal.
Too much metal in a welded joint can cause problems for your welding project because you have to stop, grind it up and clean the metal before you can start welding again. Pulse settings allow you to better control the welding process without compromising the strength and integrity of the weld.
When You Need a Neat Weld Seam
Pulse welding is an easy way to create a smooth, neat weld seam for TIG welding applications. Putting yourself in a steady pulsing rhythm is the ideal way to keep the puddle moving forward or to move the weld cup along the weld joint.
TIG welding is most often used in situations where tolerances are tight and the metal is particularly thin. By pulsing along the weld, you can adjust the amount of filler metal added so that it is evenly distributed and creates an aesthetically pleasing weld.
Minimal Movement
If you are in a tight location where you don't have much room to move, your TIG welder is able to slide along the weld seam and you can add filler metal at any time without worrying about introducing too much heat and filler. The main purpose of this application is to hold the torch steadily and apply filler metal evenly.
If this is a particularly compact area, you can pick a shorter torch with a very small head that can fit into a variety of spaces. With TIG welding, you can get into tight places better than with a stick torch, and you can control the filler metal input better than with MIG, which makes it a good choice when welding is particularly challenging.
High-speed Pulses Move Faster
According to some practices, many welders can weld efficiently at high speeds of 150 pulses per second, creating neat welds in less time. You won't want to try faster pulse speeds if you're not used to them, but many welders prefer to move at very slow or very fast speeds to create a consistent rhythm. Pulses of about 20 per second allow some welders to make uneven spot welds.
This is especially useful in fabrication shops where you will see many of the same metal pieces over and over again. If you master the speed at which you move through each part, you may be able to increase the pulse rate to improve your welding speed.
Welding Along Edges or Holes
If you need to weld quickly and cleanly without breaking an edge or filling a hole with filler metal, pulsing is another great way to give you extra control and accuracy in difficult weld locations. Without a good steady pulse during TIG welding, heat builds up and starts to melt the metal.
Are you interested in learning more about Ac pulse TIG welders for sale? Contact us today to secure an expert consultation!
 Previous:
What is TIG Welding?
Previous:
What is TIG Welding?