Plasma Cutting Machine – Its Working and Uses
 Nov. 25, 2024
Nov. 25, 2024
Plasma cutting is a thermal cutting technique widely used to cut or engrave materials like metals. It is one of the fastest methods available, offering high-quality, precise cuts without causing damage to the material. Despite its popularity in metal fabrication, many people are not fully familiar with plasma cutting. If you're interested in learning more about this advanced cutting technique, this post will provide you with detailed information about plasma cutting machines.
What is Plasma?
To understand how a plasma cutter works, it's essential to first understand plasma. While we are familiar with the three common states of matter—solid, liquid, and gas—plasma is the fourth state. Plasma can be found in everyday items like fluorescent lamps, televisions, and, of course, plasma cutters. Plasma is often referred to as an ionized gas because it forms when a gas is heated to extremely high temperatures or exposed to an electromagnetic field, causing the gas to become electrically conductive. This ability allows plasma cutters to effortlessly cut through metals like brass, aluminum, steel, and copper with minimal resistance.
Working Principle:
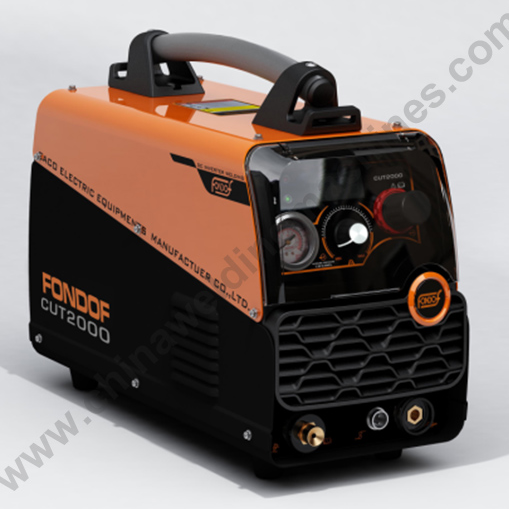
A Plasma Cutting Machine operates by using ionized gas (plasma) to cut through conductive materials. It involves a power supply, gas flow, plasma generation, a plasma torch, and the cutting process. The intense heat of the plasma melts the material, while the gas stream blows away the molten metal, creating the cut. Advanced systems may include CNC control for automated precision. This technology is widely used in industries like fabrication and metalworking for fast and accurate cutting.
How Does a Plasma Cutting Machine Work?
A plasma cutting machine uses ionized gas (plasma) to cut through conductive materials. The process involves several key components: a power supply, gas flow, plasma generation, a plasma torch, and the cutting process itself. The plasma generates intense heat that melts the material, while a focused gas stream blows away the molten metal, creating the cut. In advanced systems, CNC control is often integrated for automated, precise cutting.
Plasma cutting is an efficient method for cutting both thin and thick materials. Its high speed and precision make it a popular choice in industries such as automotive repair, industrial construction, manufacturing, salvage, and scrapping, where fast and accurate cuts are essential.
How to Use a Plasma Cutting Machine Effectively?
Now that we’ve covered the basics of how plasma cutters work, let’s explore how to maximize their effectiveness.
Field Uses: Plasma cutters come in a range of models, from budget-friendly to high-end options. Most of these machines are performance-driven and can be tailored to meet specific needs. For field use, a machine with 15 to 20-foot leads is ideal, allowing you to get the job done efficiently while saving on air and electricity.
Shop Uses: Plasma cutters are commonly found in workshops, often integrated with computer numerical control (CNC) machines for automated precision. This setup allows you to transform raw sheets of metal into finely crafted pieces, with accurate and repeatable cuts. While manual cutting can be tedious and prone to errors, plasma cutters provide consistent results, improving productivity and quality.
Other Uses: Plasma cutters are also versatile tools for a variety of projects, such as art installations, home renovations, and repairs. They enable you to cut small metal pieces quickly and precisely, saving you time and effort without needing to go to a shop. Whether you're working on creative designs or fixing metal components, a plasma cutter can streamline the process.