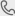Is Air or Nitrogen Better for Air Plasma Cutting Machine?
 Jul. 05, 2023
Jul. 05, 2023
When it comes to plasma cutting, the choice between air and nitrogen as the plasma cutting gas depends on various factors, including the specific application, material being cut, desired cut quality, and cost considerations. Let's delve deeper into the characteristics and benefits of both air and nitrogen as plasma cutting gases:
Air Plasma Cutting:
Air is the most common and easily accessible plasma cutting gas. It is composed primarily of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), with trace amounts of other gases. Air plasma cutting offers several advantages:
1. Cost-effective:
Air is readily available and generally less expensive compared to other gases, including nitrogen. This makes it a cost-effective option for many applications.
2. Convenience:
Air plasma cutting machines do not require an additional gas supply or storage system beyond a standard air compressor. This convenience and simplicity in setup and operation make air plasma cutting widely adopted.
3. Versatility:
Air plasma cutting is suitable for a wide range of materials, including mild steel, stainless steel, and aluminum. It provides satisfactory results for general-purpose cutting applications.
4. Cutting Speed:
Air plasma cutting can achieve faster cutting speeds compared to other methods like oxyfuel cutting. This efficiency is beneficial for large-scale industrial operations with high production volumes.
However, there are limitations to air plasma cutting:
1. Cut Quality:
Air contains oxygen, which can lead to an oxidizing effect on the cut edge. This can result in increased bevel angles and potential dross formation, leading to reduced cut quality, especially when precision and smoothness are crucial.
2. Thinner Materials:
Air plasma cutting may not provide optimal results on thinner materials due to the larger heat-affected zone and potential distortion caused by the higher energy density. In such cases, alternative gases like nitrogen are often preferred.
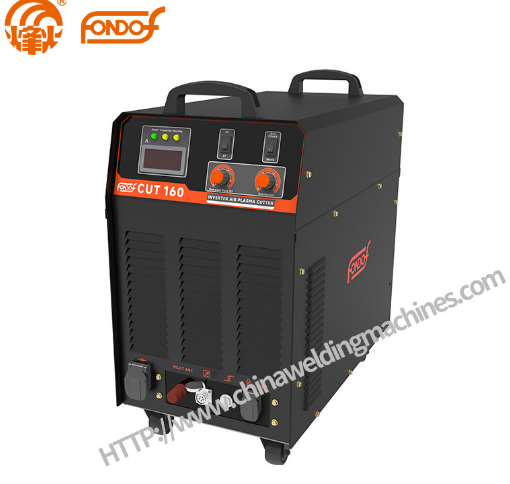
Air Plasma Cutting Machine CUT 160
Nitrogen Plasma Cutting:
Nitrogen is an inert gas commonly used as a plasma cutting gas, especially when higher cut quality and precision are desired. Here are the benefits of nitrogen plasma cutting:
1. Cut Quality:
Nitrogen plasma cutting produces cleaner cuts with minimal oxidation compared to air plasma cutting. The absence of oxygen results in reduced bevel angles, improved edge quality, and minimal dross formation. This is particularly important for applications requiring high-quality finishes and precise cuts.
2. Narrow Kerf Width:
Nitrogen's inert properties allow for a narrower kerf width during cutting. This leads to reduced material wastage, making it advantageous for applications where material optimization is a priority.
3. Thinner Materials:
Nitrogen plasma cutting is well-suited for cutting thinner materials with higher precision and minimal distortion. The reduced heat-affected zone and lower energy density of nitrogen plasma cutting make it a preferred choice for intricate and detailed cutting operations.
However, there are considerations with nitrogen plasma cutting:
1. Cost:
Nitrogen gas is typically more expensive than air. It requires a separate gas supply system and storage, contributing to higher operating costs. The increased expense is often justified by the improved cut quality and precision achieved with nitrogen.
2. Availability:
Nitrogen may not be as readily available as air in all locations. Depending on the region, the accessibility and cost of nitrogen supply can vary, and this should be taken into account when deciding on the cutting gas.
Conclusion
In summary, the choice between air and nitrogen as plasma cutting gases depends on the specific requirements of the application. Air plasma cutting machine is cost-effective, convenient, and suitable for general-purpose cutting of various materials. On the other hand, nitrogen plasma cutting provides superior cut quality, narrower kerf width, and precise cutting of thinner materials, albeit at a higher cost. Considerations should be made based on the desired cut quality, material thickness, and budget to determine the most suitable option for a particular plasma cutting application.