How Does AC Welding Work?
 Feb. 22, 2023
Feb. 22, 2023
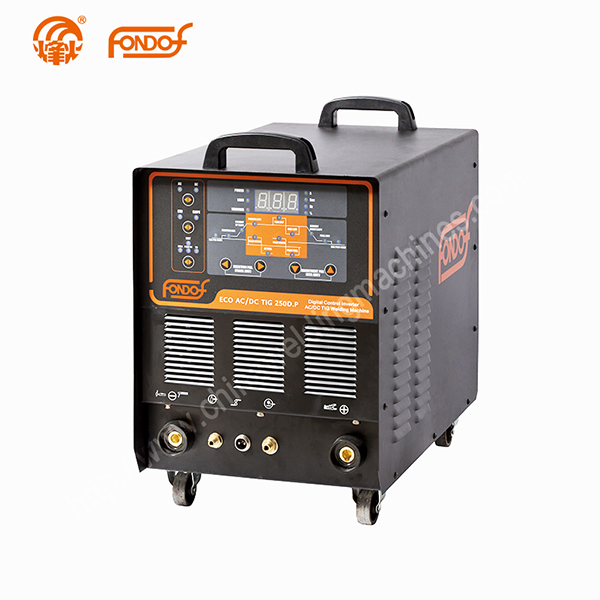
AC welding, also known as Alternating Current welding, is a welding process that utilizes a current that periodically changes direction. It is commonly used in various industries such as construction, automotive, and manufacturing due to its versatility and effectiveness.
In this article, we will discuss how AC welding works.
First, let us understand what welding is. Welding is a process of joining two or more pieces of metal by melting them together. The goal is to create a strong bond between the pieces of metal that is as durable as the original metal. Welding can be achieved through various techniques such as gas welding, arc welding, and resistance welding.
AC welding is a type of arc welding, and it utilizes a power source that produces an alternating current. The power source is connected to an electrode holder, which holds the welding electrode. The welding electrode is made of a metal rod coated with a flux material.
When the welding process starts, the electrode is brought into contact with the metal to be welded, and an electric arc is created between the electrode and the metal. The heat generated from the electric arc melts the metal and the electrode, creating a molten pool.
During AC welding, the alternating current periodically changes direction, and this creates a unique effect on the welding process. The direction of the current affects the melting and solidification of the metal being welded.
In the first half of the cycle, the current flows in one direction, and this causes the electrode to heat up and melt. The molten metal from the electrode mixes with the metal being welded, creating a weld pool. As the current direction changes, the electrode cools down and solidifies, and the molten metal solidifies and fuses with the metal being welded.
During the second half of the cycle, the current flows in the opposite direction, and this causes the metal being welded to heat up and melt. The molten metal from the metal being welded mixes with the molten pool, creating a strong bond between the two pieces of metal.
This alternating cycle of heating and cooling creates a unique effect on the welding process. It allows for the creation of a deep weld that penetrates the metal, creating a strong bond. Additionally, the alternating cycle of heating and cooling creates less deformation in the metal, which is an advantage for welding thin sheets of metal.
The flux coating on the electrode also plays a vital role in the welding process. The flux coating helps to protect the weld from oxidation and contamination. It also creates a shielding gas that protects the weld from air, water vapor, and other contaminants that could weaken the weld.
In summary, AC welding is a welding process that utilizes an alternating current to join two or more pieces of metal. The alternating current causes the metal being welded and the electrode to heat up and cool down, creating a deep weld that penetrates the metal and creates a strong bond. The flux coating on the electrode helps to protect the weld from oxidation and contamination, creating a durable and long-lasting bond between the pieces of metal. For more information, please contact us. We will provide professional answers.
 Previous:
What is Air Plasma Cutting Machine?
Previous:
What is Air Plasma Cutting Machine?