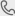AC Welding Machine
What is welding?
Welding is a process of joining metals together by melting parts and using fillers to form joints. Welding can be done using different energy sources, from gas flame or electric arc to laser or ultrasonic. It is not possible to weld all types of metals. For example, stainless steel is prone to cracking and deforming when overheated. Alloys are often a problem because it is difficult to know the exact chemical composition of the metal.
If a welder wants to make the best welding, he must understand the meaning of alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) to the welding machine and electrode.
What do ac and dc mean?
Electricity flows in two ways: alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC). Electricity or "current" is nothing more than the movement of electrons through a conductor (such as a wire). The difference between AC and DC is the direction of electron flow. In DC, electrons flow steadily in a single direction or "forward". In alternating current, electrons constantly switch directions, sometimes "forward" and then "backward".
Alternating current is the best way to transmit power over long distances.
AC and DC are terms referring to the polarity of the current generated by the welding machine and flowing through the electrode.
Welding strength depends on the choice of electrodes with the correct polarity, because the polarity of the electrode will significantly affect the welding strength and welding quality
Welding machines AC
Alternating current (AC) is electricity that switches direction back and forth, so the voltage will also periodically reverse as the current changes direction.
In this section, we will refer to welding machines that use electrodes and that only have AC (alternating current) output.
The welding quality of this type of machines is not optimal, not by the operator, but by the output of the current.
This type of welding machines with only AC (alternating current) output, as the name implies, causes the current to alternate in time. Since is not a constant current, the delivery of heat varies over time.
These would be asymmetric, since the current varies from positive to negative and that is perceived in the welding, in the electric arc.
When this happens, not having a weld arc or a constant heat delivery, that makes the operator try harder so the welding is well done.
To solve this, it is best to have equipment that is both AC and DC (direct current), because the latter, being a constant current, provides a fixed power that allows to have homogeneous cords.
DC welding machines
Direct current (DC) is current that flows in a constant direction and/or has a voltage of constant polarity (positive or negative). Typical DC devices include batteries, which are commonly used in low-voltage devices such as cell phones and remote controls.
AC machines are widely used by those who work with welding because they are the most cheap in the market. But they are not necessarily the machines with greater performance and better results when working.
Although the price difference is not much, for a better equipment that has a DC output, an additional investment is needed.
Among the benefits obtained when working with a DC welding machine, apart from the welding stability, is that long, homogenous cords can be made, decreasing or eliminating the probabilities of defect in the welding.
There is greater control of the heat generated on the piece, which can even be regulated, due to the greater control in the current, because it is direct.
Another benefit of DC welding machines is that can be adapted a welding process known as TIG or Argon, or even other processes that would not be possible in AC welding machines.
Even more, the recommendation is not to use AC welding machines but only DC, like the inverting machines, which are used a lot today due the comfort of work they offer, the possibility of working at heights and the stability in the current.
That is why the inverter machines do not use AC output. That output can be seen in the welding machines of previous models, such as those of the 1970s, where there were still no technologies that could make the current more stable.
Other differences between ac and dc
In AC, it is safe to transmit over longer urban distances and can provide more power, while in DC, DC voltage cannot travel very far until it starts to lose energy-energy that can be carried.
Stable magnetism along the wire, and in AC, it will rotate the magnet along the wire. Reasons for the direction of electron flow
The frequency of alternating current is 50 Hz or 60 Hz, depending on the country, while the frequency of direct current is zero. frequency
AC reverses its direction as it flows through the circuit. Direct current flows in one direction in the circuit. direction
The magnitude of the alternating current changes with time. Direct current has a constant amplitude-current.
In AC, electrons keep switching directions-forward and backward, while in DC, electrons move steadily in one direction or "forward-electron flow"
Ac has a passive parameter Impedance, while the passive parameter of Dc is only resistance
Ac is between 0 and 1. DC is always 1-power factor
The AC types are sine, trapezoid, triangle, and square. The DC type is pure and pulsating.
Ac is obtained from AC generator and power supply. Dc comes from Cells or Battery
Read More